Introduction
Scaffolding is key in construction, but safety is critical. OSHA sets rules to protect workers. These rules cover scaffold building, inspection, and use.There are ten main OSHA standards. These include guidelines for scaffold construction, weight limits, and fall protection. Regular inspections are also required.
Understanding these rules is important for safety. It helps avoid accidents and costly fines. You need to know how high you can build a scaffold without a license. This ensures you stay within legal limits.
Everyone on a construction site should know these requirements. This includes site supervisors and workers. Knowing and following OSHA’s scaffolding rules creates a safer workplace. Safe work practices protect lives and keep projects on track.
OSHA Scaffolding Standards & Safety Requirements
Most injuries can be avoided by following OSHA’s scaffolding safety rules. But bad habits can still cause accidents. OSHA created clear scaffolding guidelines to help businesses, especially in construction, keep workers safe.
These rules make sure that safety protocols are in place. OSHA has several key rules that employers must follow when using scaffolds. By sticking to these safety measures, employers can lower the risk of injuries. This helps create a safer work environment for everyone. Following OSHA’s guidelines is crucial to protecting workers on the job.
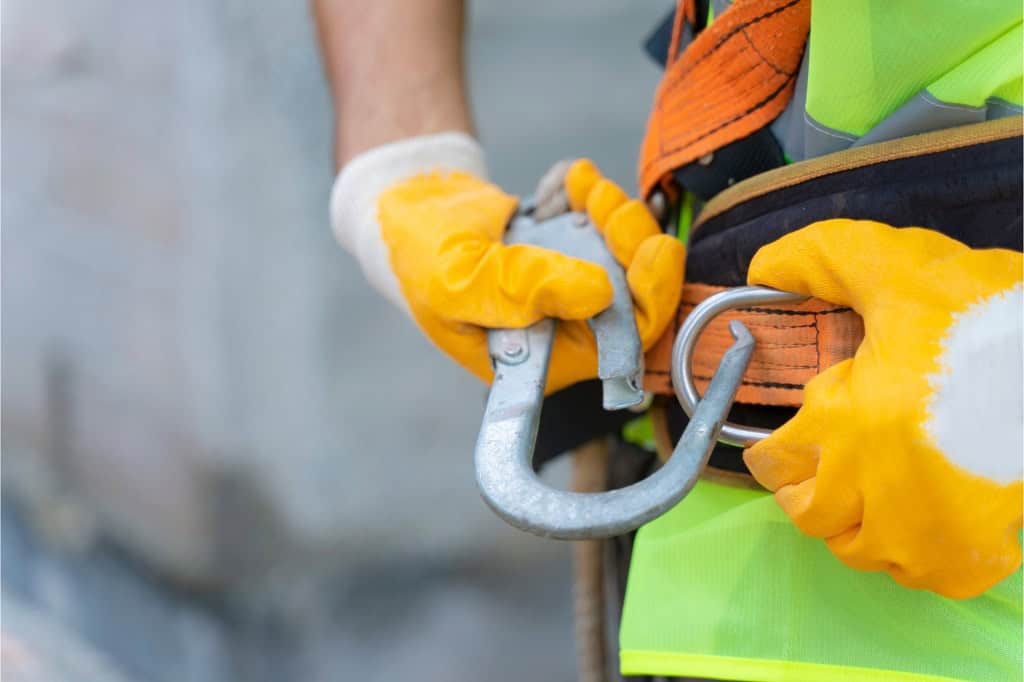

Fall Protection
When working more than 10 feet high, fall protection is essential. Workers must use fall arrest systems or guardrails. These prevent dangerous falls. Workers on single-point and two-point scaffolds need extra safety, and they must use both guardrails and a personal fall arrest system. This added protection is crucial for safety.
Guardrail Height
Guardrails prevent falls from scaffolding. They act as a barrier between workers and the edge. OSHA has strict rules for guardrail height. For scaffolds made after January 1, 2000, the toprail must be 38 to 45 inches high. For older scaffolds, it should be 36 to 45 inches. Correct guardrail height is vital for safety.
Cross Bracing
Cross bracing strengthens scaffolding by adding extra support. This method makes scaffolding more stable and sturdy. The crosspoint of cross bracing used as a top rail must be 38 to 48 inches above the platform. This helps keep the scaffold stable. Proper cross-bracing is key to preventing accidents.
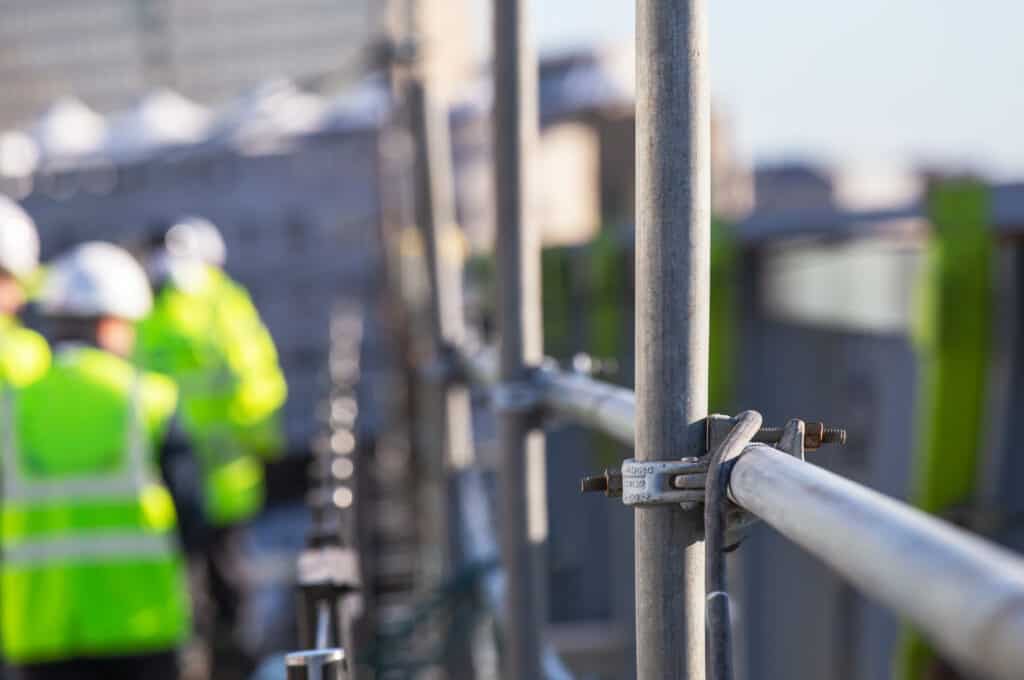

Midrails
Midrails stop workers from slipping through gaps. They are placed between the toprail and the platform. OSHA requires midrails to be halfway between the toprail and platform surface. If cross bracing is used as a mid-rail, it should be 20 to 30 inches above the platform. Proper mid-rails reduce the risk of falls.
Footings
Scaffold footings must be level and strong. They need to support the entire scaffold, including workers and tools. The legs and poles must transfer weight to the base plates and mud sills. Strong footings prevent scaffolding from tipping over. Safe footings are crucial for stability.
Platforms
Scaffold platforms should be fully planked or decked. This means no gaps that could cause tripping. OSHA requires platforms to have guardrails, midrails, and toeboards on open sides. Keep platforms clean to avoid slips. Regular cleaning and secure planking are essential for safety.
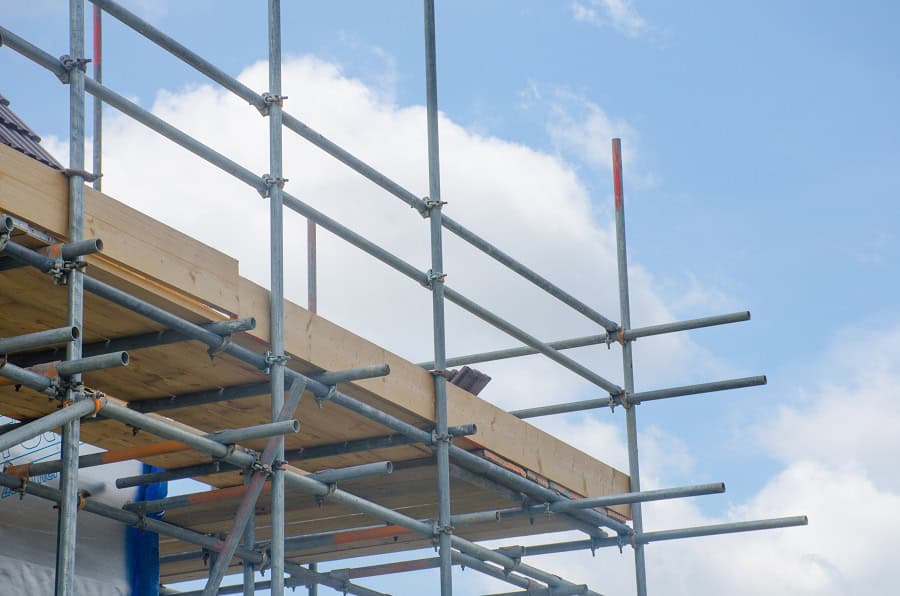

Guying, Ties, and Braces
Guys, ties, and braces stabilize scaffolding. They stop the scaffold from tipping over. Install these supports as recommended by the scaffold manufacturer. Use them when the scaffold height exceeds a 4:1 base ratio. These supports are necessary for tall scaffolds.
Capacity
Scaffolding must support at least four times the maximum intended load. This ensures it can hold workers, tools, and materials safely. Exceeding the load limit can cause scaffolding to fail. Always know the load capacity and never exceed it. Safe loading is vital.
Training
OSHA requires scaffold training for all workers. Training covers proper scaffold use and handling. Workers learn about hazards like electrical risks and falling objects. Training also includes understanding load limits. Proper training helps workers stay safe on scaffolds.

Inspections
Regular inspections keep scaffolding safe. A competent person must inspect scaffolds before each shift. Inspections check for defects that could cause accidents. Finding and fixing problems early prevents injuries.
How High Can You Build a Scaffold Without a License?
Knowing how high you can build a scaffold without extra requirements is important for safety. OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) has clear rules to guide this. These rules ensure scaffolds are safe and stable, reducing the risk of accidents.
OSHA Height Limits
OSHA allows scaffolds to be built up to 125 feet above the base without needing a special design. If the scaffold goes higher than 125 feet, more precautions are needed. At this height, a registered professional engineer must design the scaffold. The reason is simple: the higher the scaffold, the greater the risks and stress on the structure. Without a proper design, a tall scaffold could fail, leading to serious accidents.