products
Wood Scaffold Plank
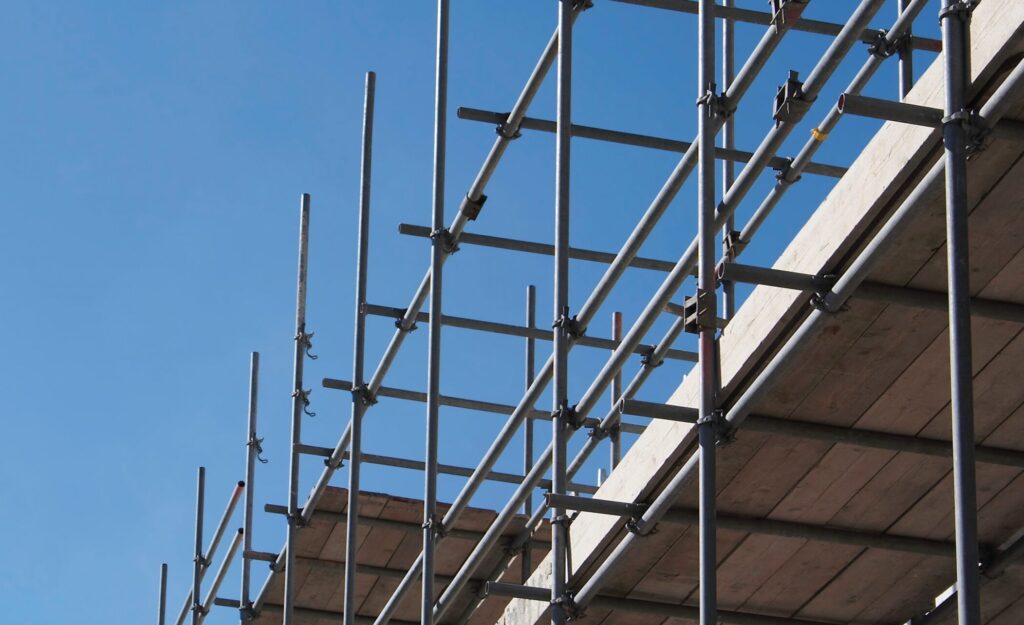
Wood Scaffold Planks are used to bridge gaps in order to provide a consistent working platform between horizontal members of a scaffold tower. These planks allow the working platform to be constructed safely and efficiently, so that they can carry out operations safely at high places.
- Rigorous quality inspection and safety testing
- Outstanding load-bearing capacity, stability and durability
- Polishing, non-slip, construction workers more secure
- Convenient installation and disassembly function
Make Workers Work Safely and Efficiently
- High strength: wooden scaffolding plates have high strength, can withstand a certain weight and pressure, so it is widely used in construction sites and decoration sites.
- Easy installation: the installation of wooden scaffolding plates is relatively simple, can be quickly set up and disassembled, without special tools and skills.
- High safety performance: wooden scaffolding plates have excellent bearing capacity and stability, can ensure the safety of workers working at high places.
- Good environmental performance: wooden scaffolding plates are a natural material, will not cause pollution to the environment, in line with the requirements of modern society for environmental protection.

components
Types of Wood Scaffold Planks We Provide
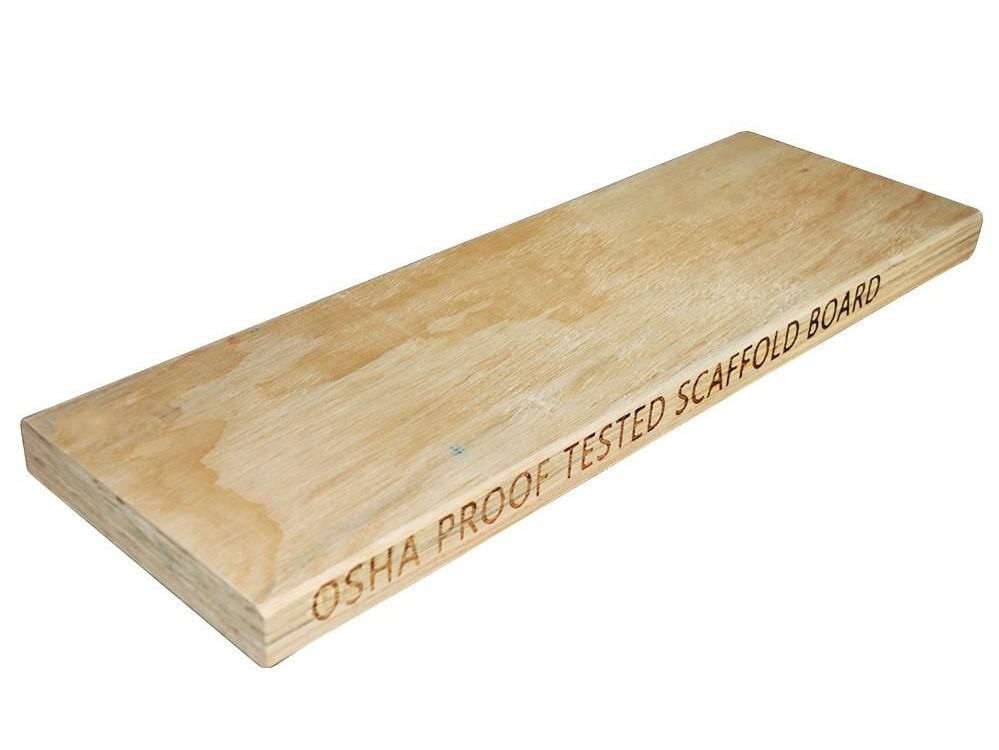

Wood Scaffold Plank
Material: Poplar; Radiata Pine; Eucalyptus; etc.
Size: 38x225x3900mm or as your need.
Glue: Melamine glue, WBP glue.

Wood Scaffold Plank with Painting
Material: Poplar; Radiata Pine; Eucalyptus; etc.
Size: 38x225x3900mm or as your need.
Glue: Melamine glue, WBP glue.

Wood Scaffold Plank with Iron Sheer
Material: Poplar; Radiata Pine; Eucalyptus; etc.
Size: 38x225x3900mm or as your need.
Glue: Melamine glue, WBP glue.
More Details

- Collect wood material: We prioritize high-quality, moisture-resistant natural wood.
- Drying: Wood veneers are drive by the drying machine.
- Angular crinding: After this way finishing, the lap joints will be the same thickness as other parts, and there will be no hole and the lap joints.
- Joint veneer: Wood veneers are jointed by workers.
- Hot press: Mat is pressed by heated steel belt.
- Cooling: Ex hot press, large size boards kept cool.
- Sanding: Board surface is sanding by sanding machine.
- Making mark: Making mark according to customers’ requirements.
- Packing: Every sheet has been carefully tested.

• Dry planks can be stacked on top of one another, well clear of the ground and covered to keep dry.
• Wet planks should be stacked in a dry, well-ventilated area clear of the ground, with spacers/fillets aligned between each layer to allow air flow to dry out the planks.
• The stack should be level, neatly stacked and supported with aligned bearers and spacers not greater than 2.0m apart.

• Do not use Scaffold Plank over greater spans than those recommended for each Duty Category.
• Do not drop or throw Scaffold Plank from excessive heights.
• Do not drive over Scaffold Plank.
• Notching, cutting or machining Scaffold Plank will reduce its strength.

- Radiate Pine veneers are largely unaffected by exposure to moderate strength acids or alkalis (in the pH range 3-9).
- Strong concentrations of acids or alkalis will affect the lignin which binds wood fibre. The phenolic resin used to bond Plank is highly resistant to chemical attack. Planks used in these conditions should be regularly evaluated before reuse.
Why Choose Us

To ensure strength and consistency, APAC maintains strict quality control standards and performance testing.
- Perfect quality control
- Advanced production equipment and facilities
- Professional team on producing, trading and shipping
Faqs
Frequently Asked Questions.

If you have any other questions about scaffolding plates, please feel free to contact us.
A risk assessment should always be conducted to determine the necessity of tying down scaffold planks, however, a good rule of thumb is that boards less than 2.13m long and under 38mm thick should be tied down to prevent tipping
OSHA’s Safety Standards for Scaffolds Used in the Construction Industry (29 CFR 1926, Subpart L, Ref. 1) has very specific requirements for the performance of scaffold planking.
Primarily, it “must be able to support, without failure, its own weight and at least four times the intended load.” Secondly, when fully loaded, the plank cannot deflect more than 1 ⁄60 of the span. Only very high quality planks are able to meet these performance standards.
Extreme Fiber Bending (Fb) is the most crucial design value and it accounts for about 65% of the planks’ overall performance. It is a measurement of the correlation of a plank’s load carrying capacity in relationship to how much the board flexes before beginning to fracture and break. The Modulus of Elasticity (MOE) is the second most important design value and is a measurement of a planks’ stiffness or rigidity. It constitutes about 30% of the planks overall performance. Given the strength differences of each and every type of plank product, it is critical you refer to the product literature provided by the mill or manufacturer for the specific plank product you are considering.
OSHA standards specify that a wood plank should extend a minimum of 6” and maximum of 12” beyond the supporting points of scaffold frame.
Solid sawn wood plank is visually graded as a whole piece, therefore it is not recommended that a plank be arbitrarily cut into smaller sections. At a shorter length, there is a possibility that defects such as knots or splits might end up being located exactly where the plank needs to bear on the scaffold frame. Since genuine OSHA recognized laminated plank is mechanically tested and the structural integrity is more predictable, cutting longer boards into shorter ones is generally not an issue. Keep in mind that older, used planks may have been compromised from prior usage and field conditions, and therefore should be inspected closely before cutting.